“Your files have been encrypted” – is undoubtedly a message that nobody wants to encounter at the beginning of their workday.
Fortunately, this instance only represents the outcome of a ransomware analysis conducted by a Guardz Cyber Intelligence Researcher (CIR) within the isolated environment offered by the Hybrid Analysis service.
What is Ransomware?
To delve straight into the matter- ransomware is a specific type of malware designed to encrypt files until the affected party pays a ransom to the attacker (essentially, a form of digital extortion).
Upon infection, the ransomware typically displays a message on the screen that contains instructions on how to pay the ransom. It may threaten to delete files permanently or increase the ransom amount if the demands are not met within a certain timeframe.
It is important to note that ransomware attacks can vary in sophistication and tactics, with new variants continually emerging over time. Cybercriminals behind these attacks constantly evolve their methods to bypass security measures and maximize their chances of success.
Some ransomware strains employ advanced techniques, such as exploiting software vulnerabilities or utilizing sophisticated encryption algorithms, while others rely on more straightforward approaches. Despite the diversity in tactics, the core concept of ransomware remains consistent across most attacks.
In this blog, Guardz CIR will cover the history of this malicious vector, discuss why SMEs are the prime targets for such attacks, and demonstrate how MSPs can leverage the Guardz insurance offering.
Additionally, we will outline the connection between ransomware and cybercrime underground forums to illustrate how these two factors are directly linked to this type of attack.
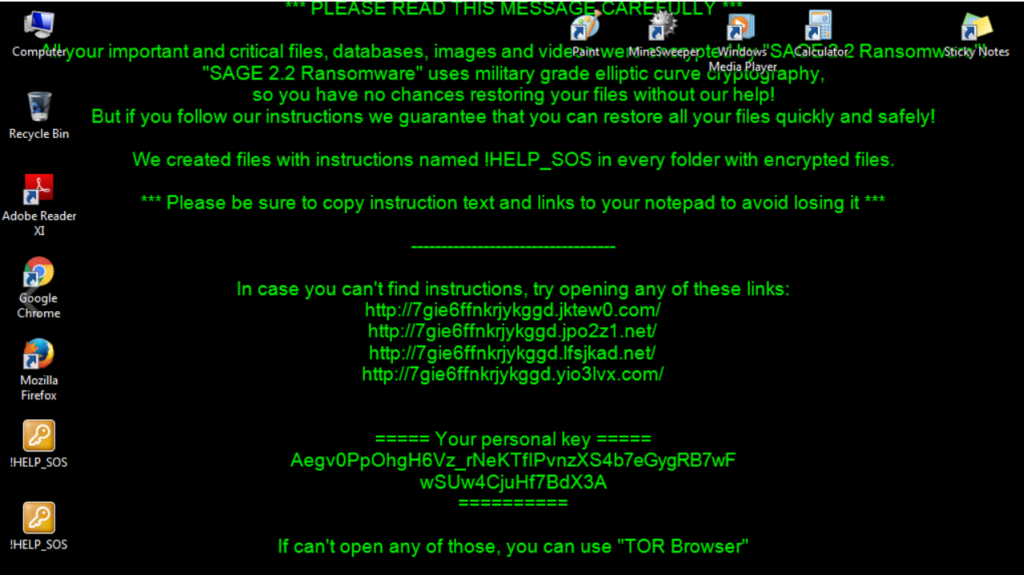
Upon infection, the ransomware typically displays a message on the screen that contains instructions on how to pay the ransom. It may threaten to delete files permanently or increase the ransom amount if the demands are not met within a certain timeframe.
The Evolution of Ransomware and Its Escalation Over Time
The first known instance of ransomware dates back to 1989, referred to as the AIDS Trojan or PC Cyborg. It was created by biologist Dr. Joseph Popp and distributed via floppy disks. The malware targeted MS-DOS systems and spread under the guise of a legitimate program related to AIDS education and research.
Upon execution, the ransomware encrypted the filenames on the victim’s hard drive and displayed a message demanding a payment of $189 to be sent to a post office box in Panama. The message threatened that if the ransom was not paid within a specific timeframe, the encryption key would be permanently deleted, rendering the files inaccessible.
Looking to boost your MSP revenue? Guardz got your back!
As time passed and digitalization grew, the first signs of ransomware being delivered digitally were discovered in the early 2000s. The ransomware was primarily distributed via email messages containing malicious file attachments.
In 2013, the emergence of CryptoLocker ransomware had a significant global impact. Notably, it was the first ransomware to demand payment in cryptocurrency. CryptoLocker encrypted the victim’s files using a strong encryption algorithm and displayed a ransom note containing instructions on making a Bitcoin payment to obtain the decryption key. This marked a significant shift in the ransomware landscape by incorporating Bitcoin as the preferred payment method.
However, the ransomware threat landscape underwent another transformation in mid-2019 and skyrocketed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The notable change was that threat actors began forming ransomware gangs, moving away from the average $300-$500 ransom payment, and starting to base their ransom demands on a percentage of the targeted company’s revenue. This approach was combined with double and subsequent triple extortion methods, which we explore later in this blog.
Over the last three years, dozens of similar ransomware gangs initiated their operations and continue to be active today.
Double and Triple Extortion Concepts
Double extortion, also known as “name-and-shame” attacks, pioneered by the ransomware group “Maze,” has left a lasting impact on the ransomware landscape.
Maze ransomware operators infiltrate a victim’s network, first exfiltrating sensitive data before deploying encryption. They then threaten to publish the stolen data if the ransom remains unpaid. This dual-pronged tactic adds an extra layer of pressure on victims, encouraging them to comply with the ransom demands.
As a result, the double extortion approach has become increasingly popular among ransomware groups, who adopt this strategy to maximize profits and gain greater leverage over their victims.
Triple extortion goes a step further, involving not just the primary victim but also third-party companies or individuals affected by the cyber incident. Ransomware gangs demand payment from these parties to prevent their specific data from being published on shame sites.
While several ransomware gangs have adopted this method, Guardz CIR has observed that most malicious actors primarily employ double extortion, likely due to cost-efficiency reasons.
Empowering MSPs with AI-Driven Cybersecurity:
Secure SMBs like Never Before
“Shame” Sites
Ransomware shame sites, also known as leak sites or leak blogs, are web platforms on the Dark Web where cybercriminals publicly disclose sensitive or confidential information stolen from their victims during a ransomware attack.
When a victim organization refuses to meet the ransom demands or fails to negotiate with the attackers, the cybercriminals may choose to publish the stolen data on these shame sites or offer it for sale.
In the screenshot below, we can see examples of companies that refused to pay, resulting in their data being fully published and available for download. Conversely, other companies still have time to determine their next steps.
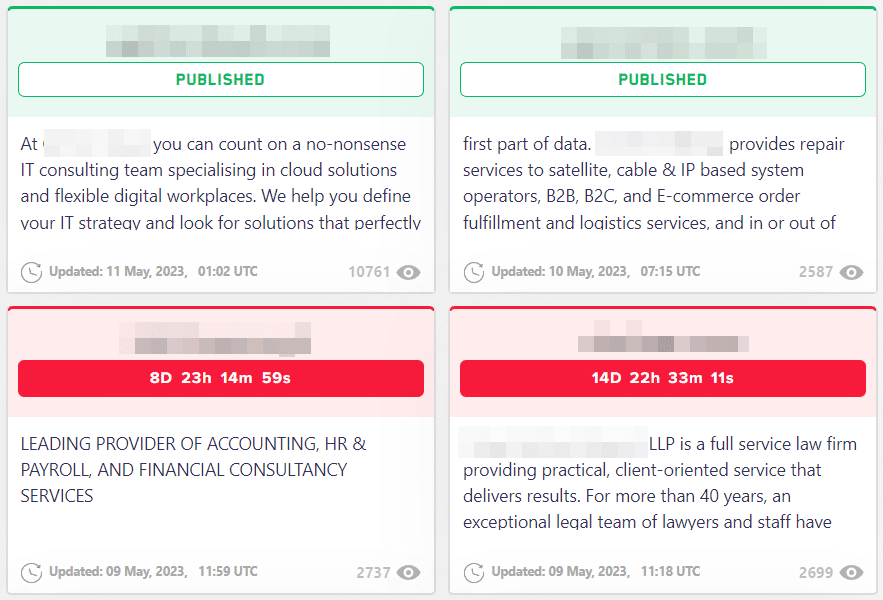
The disclosed information can encompass a wide range of data, including customer records, financial documents, intellectual property, employee details, or any other sensitive information that attackers perceive to have the potential to inflict significant harm or embarrassment upon the targeted organization.
Guardz CIR closely monitors and tracks numerous shame sites. To highlight the gravity of this issue, we have decided to analyze a shame site associated with the notorious ransomware gang “LockBit 3.0.”

As of mid-May 2023, LockBit 3.0 has successfully attacked, exfiltrated data, and encrypted over 300 companies worldwide. Companies that refused to pay the ransom discovered that their stolen information was leaked on the LockBit 3.0 shame site, further exacerbating the consequences of the attack. Other companies still have some time to decide regarding their actions to prevent this incident.
In certain unique cases, the data is offered for sale and can be purchased by an individual or competitor. Cybercriminals also provide options to request data deletion or extend the deadline.
Upon clicking one of these options, the shame sites redirect users to a payment page and provide instructions on contacting the gang via TOX messenger for further information.
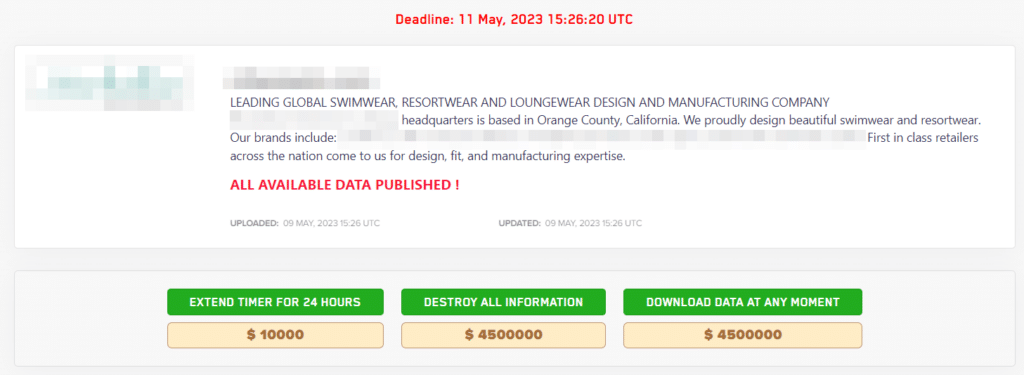
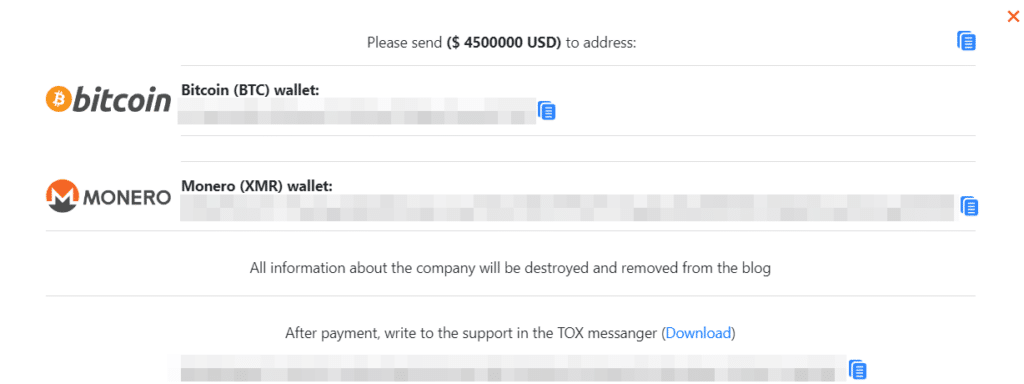
Interestingly, this particular shame site does not feature any Fortune 500 companies. Instead, the vast majority of the attacked companies are small and medium enterprises. Guardz CIR conducted a focused analysis on randomly selected companies targeted by the gang in May 2023, and here are the results.
To protect the victims’ privacy, Guardz CIR has redacted the company names and only retained general information for reference.
As evident from the analysis, all industries and company sizes have been impacted by this malicious trend.
May 2023
| Company | Region | Area | Employees | Revenue |
| 1 | EMEA | Membership Organizations | 26 | <$5M |
| 2 | USA | Automotive Service & Collision Repair | 25 | <$5M |
| 3 | LATAM | Consumer Services | 81 | $10.2M |
| 4 | LATAM | Industrial Automation | 250 | $25M |
| 5 | EMEA | Business Services | 43 | $11.8M |
| 6 | USA | Colleges & Universities | 204 | $33.2M |
| 7 | USA | Retail | 337 | $86.3M |
| 8 | EMEA | Minerals & Mining | 921 | $203.6M |
| 9 | USA | Electricity, Oil & Gas | 1880 | $592.7M |
| 10 | USA | Automotive Parts | 43,000 | $12.7B |
SMEs are Easy Targets for Ransomware
It’s crucial to comprehend that most cases begin with the malicious actor gaining access to a company’s network and successfully performing lateral movement to locate sensitive data.
Guardz CIR discussed in previous blogs how modern cyber-attacks operate using a “contractor” approach, whereby individual threat actors are responsible for separate steps in the process.
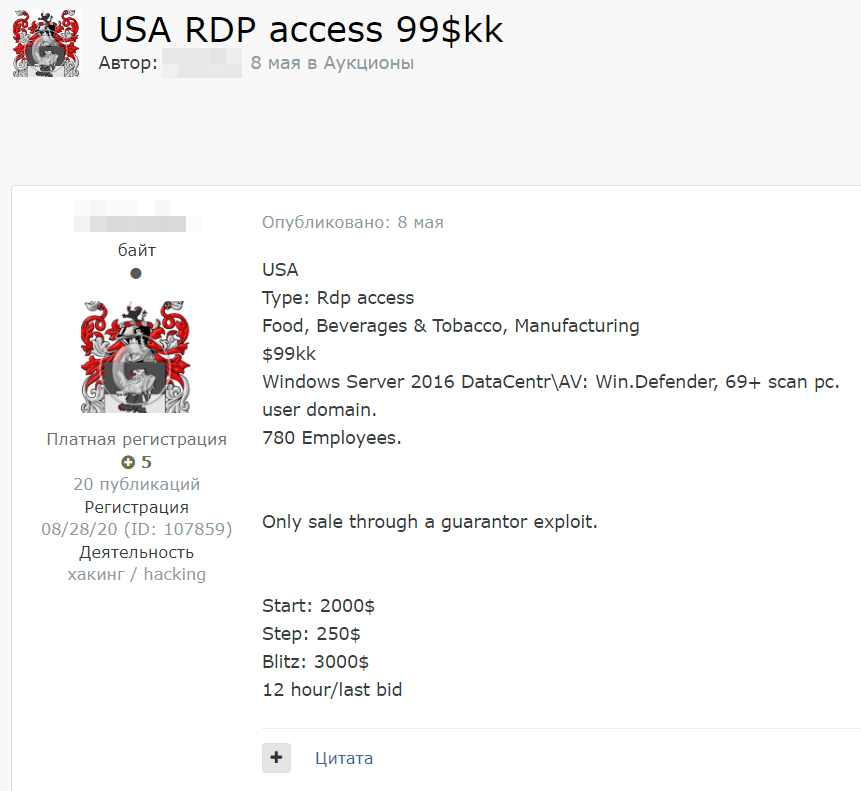
For several years, two prominent Russian language cybercrime forums have maintained dedicated sections where cybercriminals can sell compromised accesses to companies. These forums typically utilize an auction concept akin to eBay for these transactions.
Let’s look at a fresh example. For an initial price of $2000, or via the “buy it now” option for $3000, any underground forum member can acquire remote desktop access (RDP) to a US-based company with 780 employees.
The threat actor also mentions the company’s revenue ($99M) and industry – two crucial factors that determine the potential ransom amount in the event of a ransomware attack.
Guardz CIR analyzed both underground forums featuring such activity and arrived at a solid conclusion: the primary types of companies being traded on these platforms are SMEs.
Transfer the Risk
In an era of growing cyber threats and potential data breaches, cyber insurance has emerged as a crucial asset for businesses seeking to protect their digital assets and mitigate financial risks. By integrating cyber insurance into existing security measures, businesses can transfer the risk associated with cyberattacks, data breaches, phishing, ransomware attacks, and other cyber threats, ensuring insurance readiness and access to adequate tailored coverage, which is a benefit that Guardz offers as part of their comprehensive cybersecurity solution.
Cyber insurance offers an added layer of protection and financial coverage for businesses in the unfortunate event of a cyber incident.
Securing the right insurance coverage can help alleviate these financial pressures and ensure that the affected organization recovers more swiftly and efficiently.
Another invaluable aspect of cyber insurance lies in the coverage of third-party liabilities. A data breach or cyber incident affects not only the targeted organization but also its clients, customers, or business partners. Providing coverage for such liabilities ensures comprehensive protection in an increasingly interconnected world.
Summary
Global law enforcement agencies have made invaluable efforts in tracking and seizing ransomware gangs such as Hive, DoppelPaymer, and NetWalker. However, ransomware remains a persistent threat, and business owners, IT professionals, and MSPs must stay vigilant.
The cybercrime underground continues to trade compromised accesses, which can serve as an initial entry point for attackers. Additionally, insufficient cybersecurity awareness and training in the SME sector can result in significant cyber incidents.
We have also learned that the objective behind ransomware shame sites is to reveal victim vulnerabilities and potentially harm their reputation. By publicly disclosing stolen data, cybercriminals aim to pressure victims into paying ransoms quickly to avoid further exposure or misuse of the data.
Fears of reputational damage, regulatory penalties, legal ramifications, or loss of customer trust may prompt some organizations to contemplate paying the ransom. This emphasizes the importance of robust cybersecurity practices and considers cyber insurance as added protection against such threats.
Demonstrate the value you bring to the table as an MSP, Book a Demo.
- Share On:












